Amazing technological breakthrough possible @S-Logix
pro@slogix.in
To implement the binomial distribution using python.
Import libraries.
Assume sample data in a interval.
Assume n and p value.
Assume total number of samples.
Import binomial function from scipy stats.
#import libraries
from scipy import stats
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#assuming value
total_sample=10
p_value=0.4
n=np.arange(0,20)
#import binomial function
binomial=stats.binom.pmf
(n,total_sample,p_value)
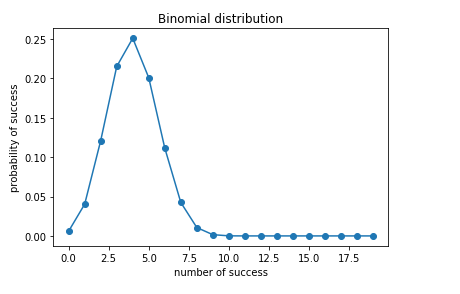
#plot the binomial distribution
plt.plot(n,binomial,’o-‘)
plt.title(“Binomial distribution”)
plt.xlabel(“number of success”)
plt.ylabel(“probability of success”)
plt.show()