Amazing technological breakthrough possible @S-Logix
pro@slogix.in
To check whether the given data set is normally distributed or not using python.
The Shapiro-Wilk normality test is reputedly more well suited to smaller data sets.
#import requires libraries
import pandas as pd
import scipy
from scipy import stats
#sample data set
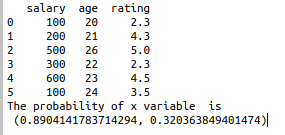
data={‘salary’:[100,200,500,300,600,100],
‘age’:[20,21,26,22,23,24],
‘rating’:[2.3,4.3,5.0,2.3,4.5,3.5]}
#load the data to data frame
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
#assigning x variable
x=(df[‘salary’])
#call the Shapiro test function
st=scipy.stats.shapiro(x)
print(df)
print(st)