To build the regression model for predicting weights of the student using student’s Height, Index in python.
Height-Weight data set. (Kaggle)
R-squared
Import keras library.
Import other needed libraries.
Load the data set.
Fix the independent and dependent variable.
Normalize the independent variable.
Split the data into train and test data.
Build the DNN model.
Compile the DNN model with appropriate loss and activation functions.
Fit the train data to the model.
Predict the test data.
Check results for new instance.
Calculate r-squared value.
#import necessary libraries
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(“ignore”)
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer
from statsmodels.graphics.gofplots import qqplot
from matplotlib import pyplot
#load the data set
data = pd.read_csv(‘…./height_weight.csv’)
#Make it as a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
#Checking missing values
print(“Checking missing values\n”)
print(df.isnull().sum())
#Pre-processing
from sklearn import preprocessing
# label_encoder object knows how to understand word labels.
label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
# Encode labels in column ‘Gender’.
df[‘Gender’]= label_encoder.fit_transform(df[‘Gender’])
#feature selection
X = df.iloc[:,[1,3]]
y = df.iloc[:,2]
#normalize the data
transformer = Normalizer().fit(X)
X = transformer.transform(X)
print(“\n”)
#Split the data into train and testing
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)
#Print training data
print(“Training data\n”,X_train,”\n”,Y_train)
print(“\n\n”)
#Print testing data
print(“Testing data\n”,X_test)
print(“\n\n”)
#create model
model = Sequential()
shape = X_train.shape[1]
#add layers to model
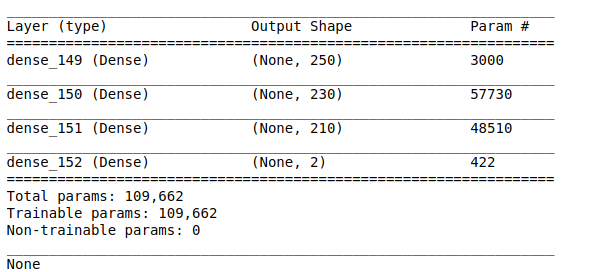
model.add(Dense(200, activation=’relu’, input_shape=(shape,)))
model.add(Dense(200, activation=’relu’))
model.add(Dense(200, activation=’relu’))
model.add(Dense(1))
print(model.summary())
#Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’, loss=’mse’,metrics=[‘accuracy’])
#Here we train the Network.
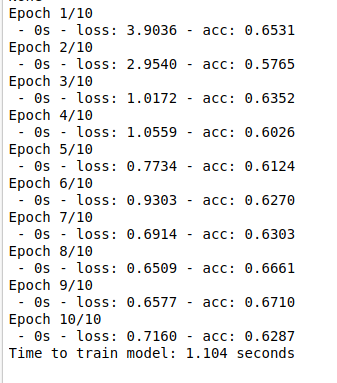
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, batch_size=30, epochs = 10, verbose = 2)
#Here we evaluate the model
score,acc = model.evaluate(X_test,Y_test,verbose = 2,batch_size = 30)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
#predict new value
print(“\n”)
new = [[174,4]]
transformer_new = Normalizer().fit(new)
new = transformer_new.transform(new)
new_pred = model.predict(new)
print(“New prediction\n”,new_pred,”\n”)
#r squared
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
R_squared = r2_score(Y_test,y_pred)
print(“R-squared\n”,round(R_squared))