To calculate the measure of dispersion for a sample data set in python.
Difference between the largest and smallest values.
It takes largest and smallest value from the data set.
It uses only the data less than 6 in a data set.
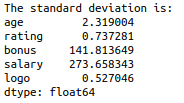
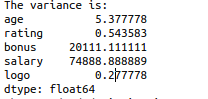
Variance measures how far a data set is spread out.
The average squared deviation of values from the mean.
It takes all data from the data set.
We can use standard deviation, if the data in a data set are more than 6.
Standard Deviation is the square root of variance.
#import pandas library
import pandas as pd
#load the data from CSV file
data=pd.read_csv(‘/home/soft27/
/Sathish/Pythonfiles/Employee.csv’)
#creating the Data Frame
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
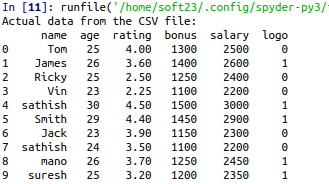
print(“Actual data from the CSV file:”)
print(df)
#Calculate the variance
print(“The variance is:”)
print(df.var())
#calculate the standard deviation
print(“The standard deviation is:”)
print(df.std())