To create a data base to store our data using python.
Install sqlalchemy package from anaconda.
Import create_engine object from sqlalchemy.
Read the data set.
Create data base engine by using create_engine method.
Store our data set to the data base using data.to_sql().
Retrieving the data using sqlite3 query.
#import libraries and sub-packages
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pandas as pd
#read the sample data set
data=pd.read_csv(‘/home/soft27/soft27/
Sathish/Pythonfiles/Employee.csv’)
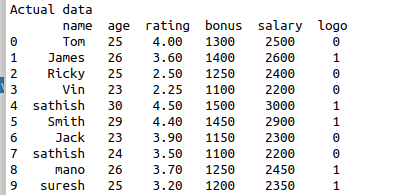
print(“Actual data/n”,data)
#Create the dtatbase engine
engine = create_engine(‘sqlite:///:memory:’)
#store the data as a table
data.to_sql(‘data_table’, engine)
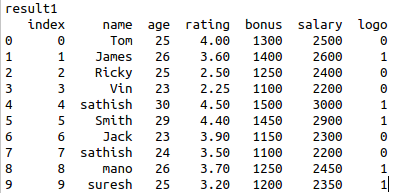
#Query 1
result1 = pd.read_sql_query(‘SELECT * FROM data_table’, engine)
print(‘result1’)
print(result1)
#Query 2
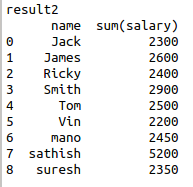
result2 = pd.read_sql_query(‘SELECT name,sum(salary) FROM data_table group by name’, engine)
print(‘result2’)
print(result2)