Research breakthrough possible @S-Logix
pro@slogix.in
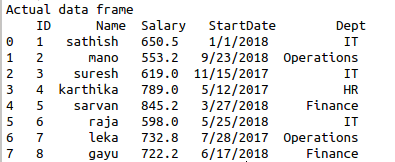
To read JSON file and select particular row and column in python.
Import pandas library.
Read the JSON file.
Store it as data frame.
Access the rows and columns of data frame using multi-axes indexing function.
#import libraries
import pandas as pd
#read the JSON file
Data=pd.read_json(‘/home/soft27/soft27/
Sathish/Pythonfiles/Employeedetails.json’)
#Create the data frame
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
#access the rows and colums randomly
print(“Accessing data from its location”)
print(data.loc[[1,3,5],[‘Salary’,’Name’]])