To locate rows or columns to define X and y variable using python.
Used to get the rows and columns with particular labels from the index.
Get rows and columns with particular positions in the index.
#import the libraries
import pandas as pd
#read the data set
data=pd.read_csv(‘/home/soft27/soft27
/Sathish/Pythonfiles/Employee.csv’)
#creating data frame
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
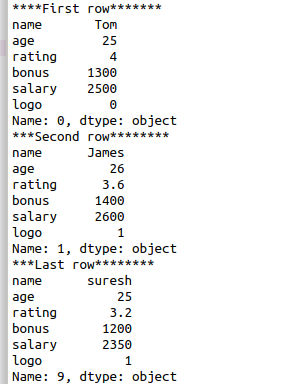
#first row of data frame
print(“****First row*******”)
print(df.iloc[0])
#second row of data frame
print(“***Second row********”)
print(df.iloc[1])
#last row of data frame
print(“***Last row********”)
print(df.iloc[-1])
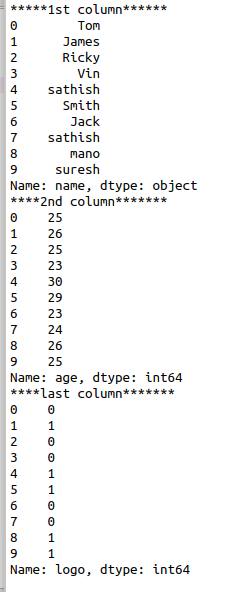
#first column of data frame
print(“*****1st column******”)
print(df.iloc[:,0])
#second column of data frame
print(“****2nd column*******”)
print(df.iloc[:,1])
#last column of data frame
print(“****last column*******”)
print(df.iloc[:,-1])