To build a DNN model for predict the alcohol level in wine data set using keras.
Wine quality data set.
MSE
MAE
Accuracy score
Load the data set.
Define the independent and dependent variable..
Build the deep neural networks.
Initiate activation and optimizer functions according to the problem.
Split the data into train and testing set.
Fit the training set into the model.
Predict the test results using DNN.
Calculate the MSE, MAE and accuracy.
#import necessary libraries
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(“ignore”)
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#load the data set
data = pd.read_csv(‘/home/soft50/soft50/Sathish/practice/winequality-red.csv’)
#Make it as a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
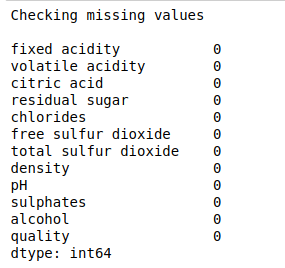
#Checking missing values
print(“Checking missing values\n”)
print(df.isnull().sum())
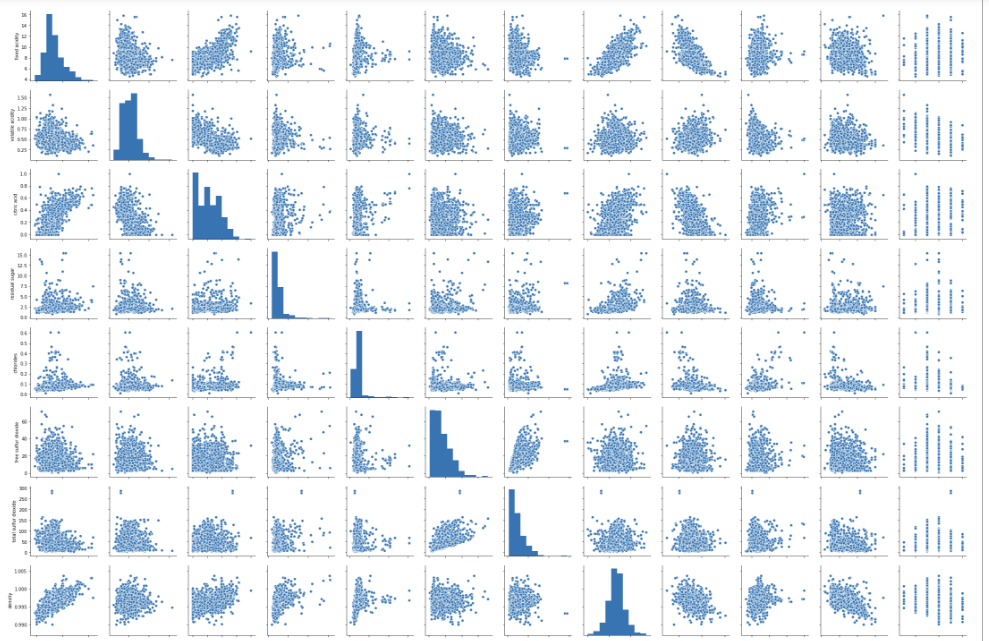
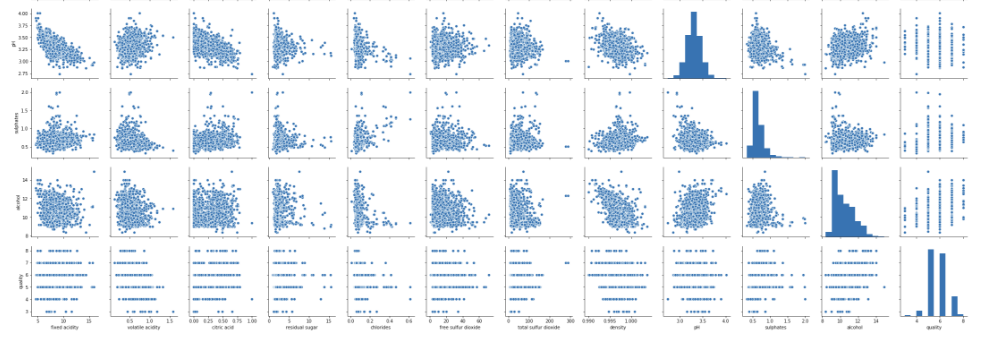
#pairplot for input variables
sns.pairplot(df)
plt.show()
#Features selection
X = data.iloc[:,0:10]
y = data.iloc[:,10].values
#Pre processing of data
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
sc= MinMaxScaler()
X= sc.fit_transform(X)
y= y.reshape(-1,1)
y=sc.fit_transform(y)
#Split the data into train and testing
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)
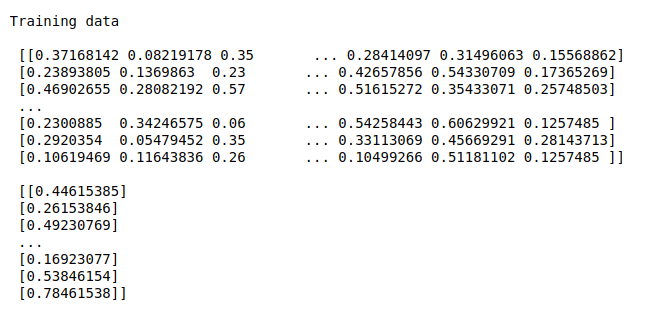
#Print training data
print(“Training data\n\n”,X_train,”\n\n”,Y_train)
print(“\n\n”)
#Print testing data
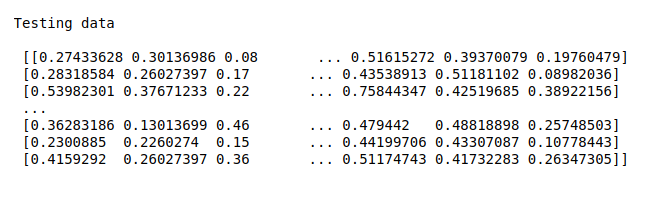
print(“Testing data\n\n”,X_test)
print(“\n\n”)
#Create DNN model for regression
dim = X_train.shape[1]
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(250, input_dim=dim, kernel_initializer=’normal’, activation=’relu’))
model.add(Dense(250, kernel_initializer=’normal’, activation=’relu’))
model.add(Dense(1, kernel_initializer=’normal’,activation=’linear’))
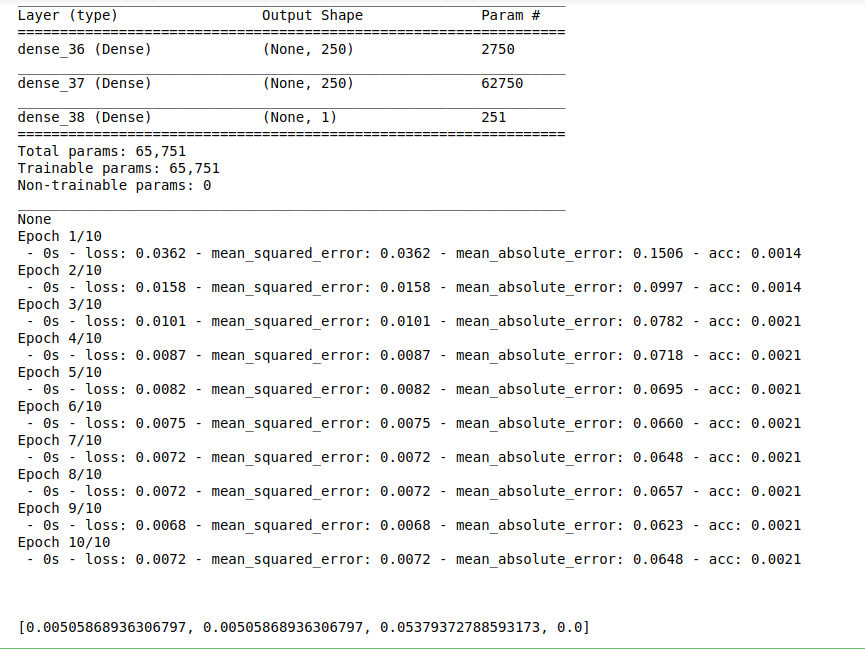
print(model.summary())
#Compile the model
model.compile(loss=’mean_squared_error’, optimizer=’adam’ ,metrics=[‘mse’, ‘mae’,’accuracy’])
#Here we train the Network.
model.fit(X_train, Y_train,batch_size=30, epochs = 10, verbose = 2)
#Here we evaluate the model
results = model.evaluate(X_test,Y_test,verbose = 2,batch_size = 30)
print(“\n\n”)
print(results)