apply() and unique() for Sample Dataset Using Python
apply() and unique() in Pythonapply() function in Pandas is used to apply a function along an axis (rows or columns) of a DataFrame or Series. This is useful when you need to perform a custom operation on each row or column.unique() function is used to return the unique values in a DataFrame column or Series. It helps to quickly identify the distinct values present in the data.
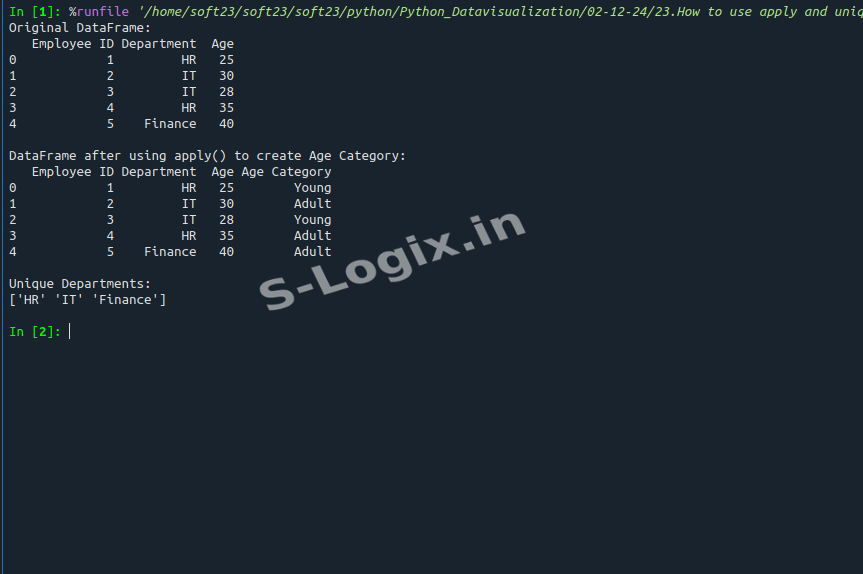
apply():apply() function to apply any custom function to each row or column of a DataFrame or Series.DataFrame.apply(func, axis=0) where axis=0 applies the function to columns and axis=1 applies it to rows.
unique():unique() function returns an array of unique values in a particular column or Series.DataFrame['column_name'].unique()
apply() to create a new column based on a custom functionapply() to create Age Category:")unique() to find the unique departments