-
STEP 1 — Create YAML File
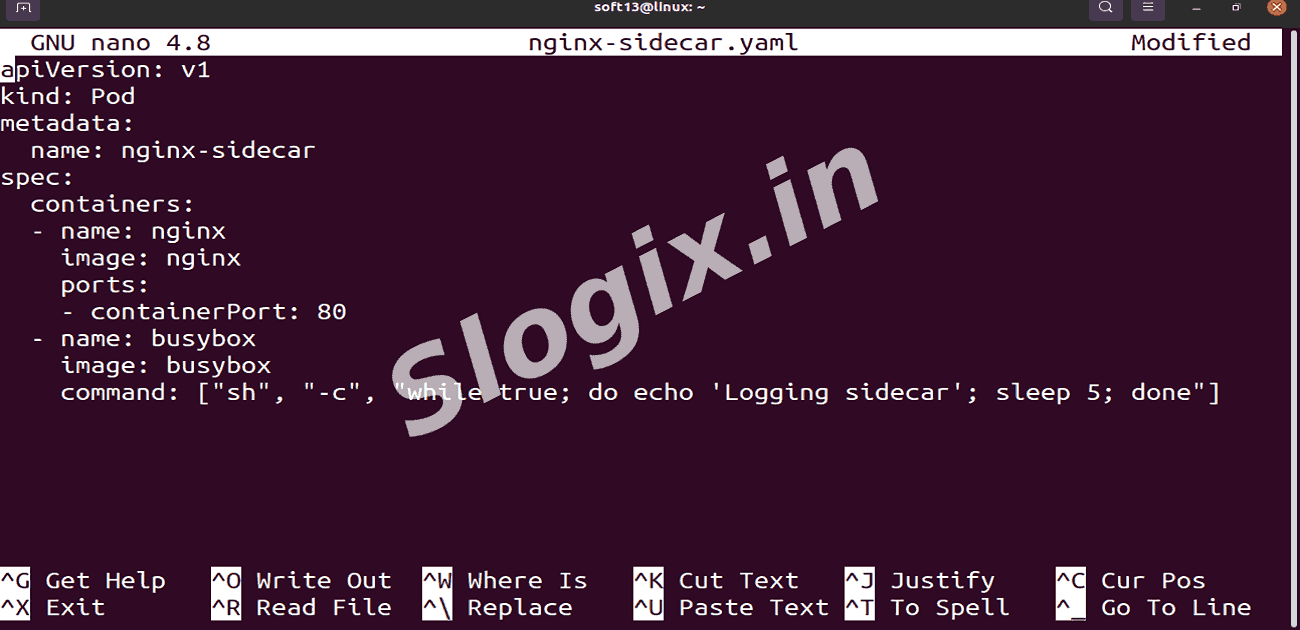
Create a file named nginx-sidecar.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-sidecar
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
- name: busybox
image: busybox
command: ["sh", "-c", "while true; do echo 'Logging sidecar'; sleep 5; done"]
-
STEP 2 — Apply the Pod
Run the following command to create the pod:
kubectl apply -f nginx-sidecar.yaml
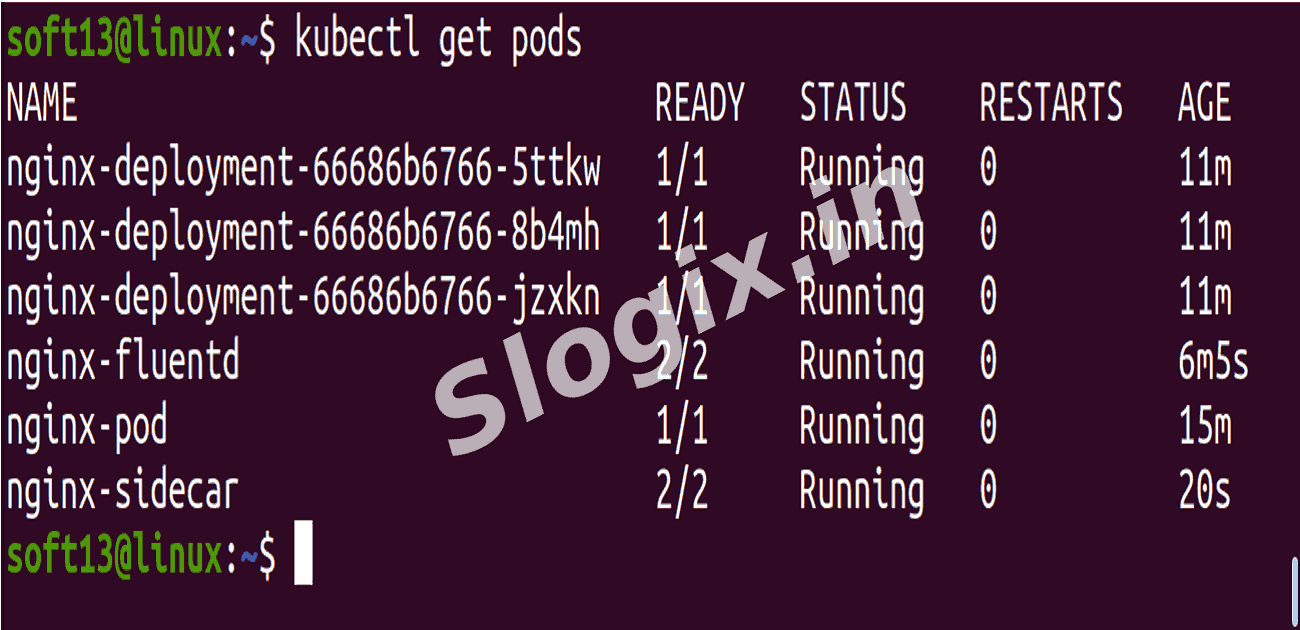
Verify the pod is running:
kubectl get pods
Check logs of the sidecar container:
kubectl logs nginx-sidecar -c busybox
-
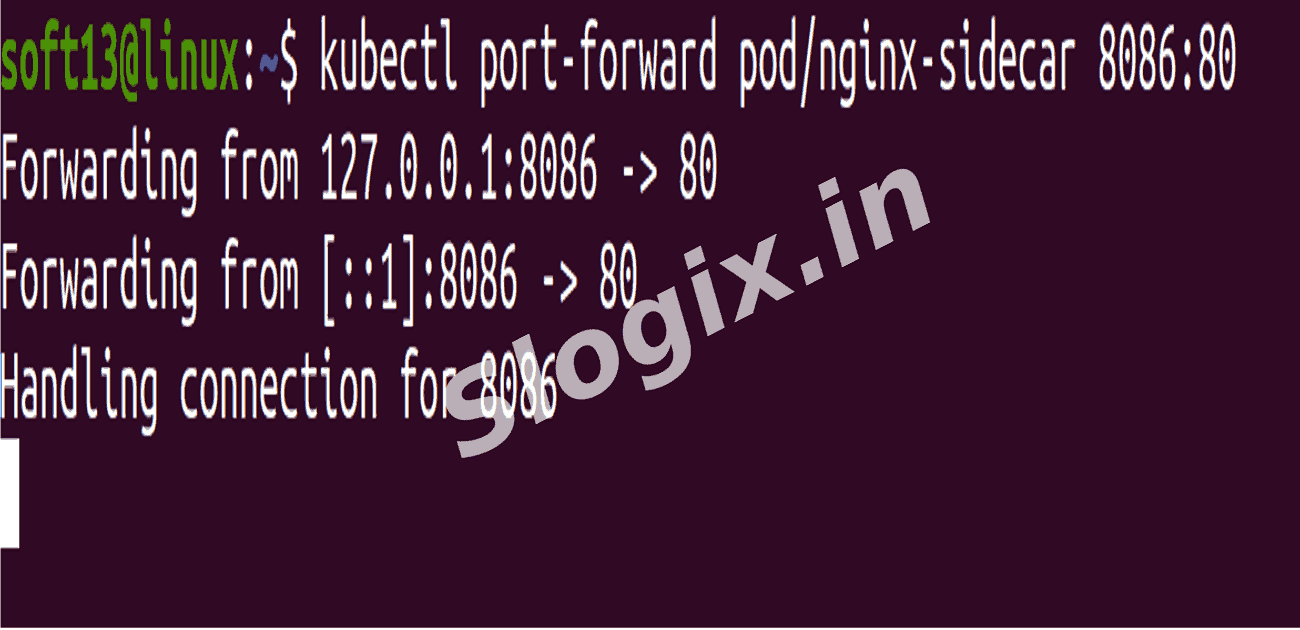
STEP 3 — Expose NGINX via Port-Forwarding
Forward port 8080 on your local machine to port 80 of the pod:
kubectl port-forward pod/nginx-sidecar 8086:80
-
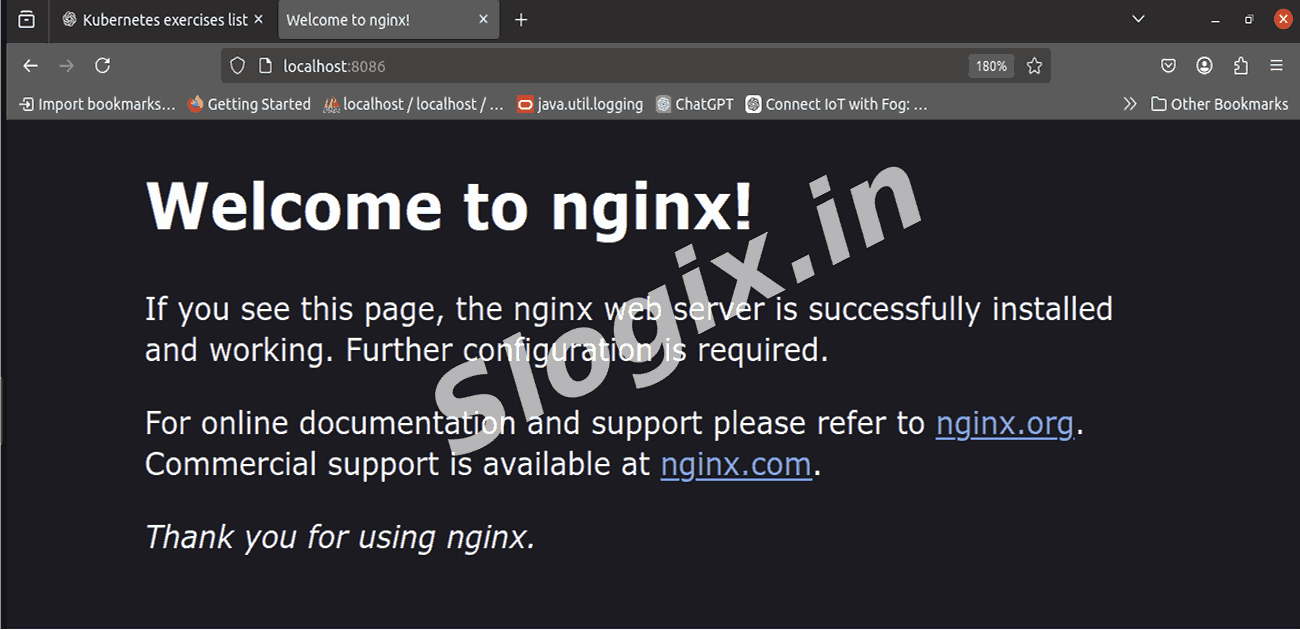
STEP 4 — Access NGINX in Browser
Open your browser and visit:
http://localhost:8080
You should see the default NGINX welcome page.
-
STEP 5 — Verify Logging Sidecar
In another terminal, check the logs of the busybox container:
kubectl logs nginx-sidecar -c busybox
You should see repeated messages:
Logging sidecar
Logging sidecar