-
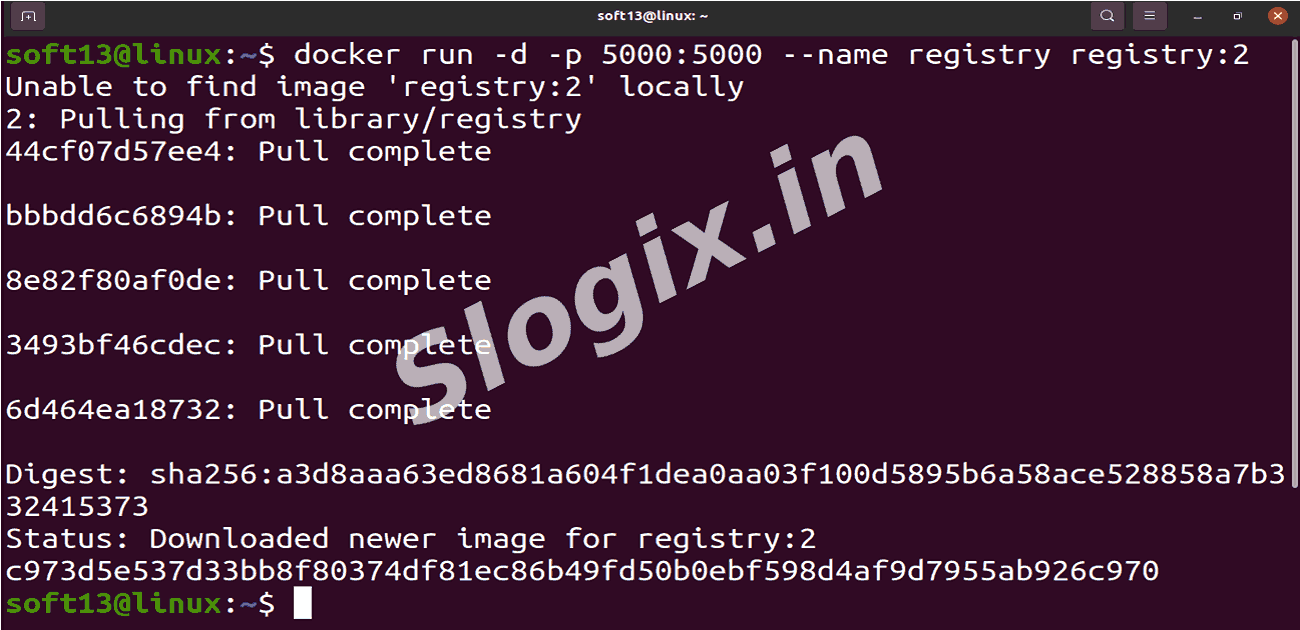
STEP 1 — Run a Private Docker Registry
Description: Start a local registry container listening on port 5000.
Command:
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name registry registry:2
-
STEP 2 — Tag an Image for the Private Registry
Description: Tag an existing Docker image to point to your local registry.
Command:
docker tag hello-docker localhost:5000/hello-docker
✔ This prepares hello-docker for pushing to the private registry.
-
STEP 3 — Push the Image to the Private Registry
Description: Upload the tagged image to your local registry.
Command:
docker push localhost:5000/hello-docker
✔ This uploads hello-docker to your private repository running on port 5000.
-
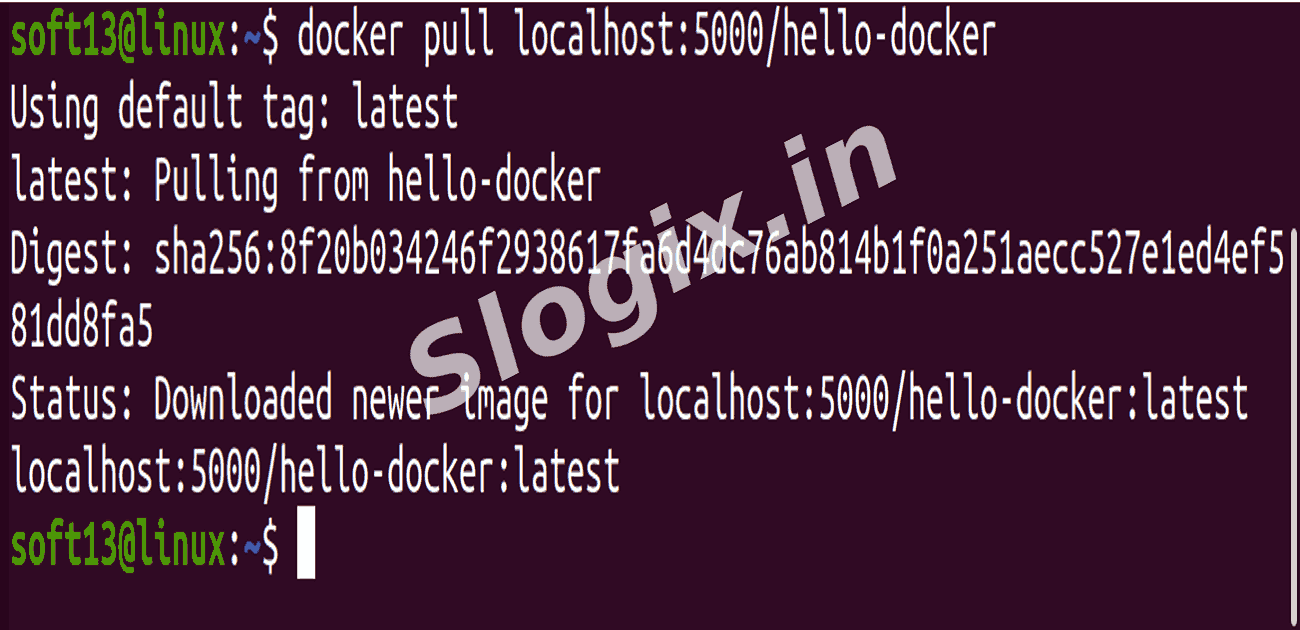
STEP 4 — Pull the Image from the Private Registry
Description: Retrieve the image from the local registry to confirm it’s stored correctly.
Command:
docker pull localhost:5000/hello-docker
-
Verification Steps
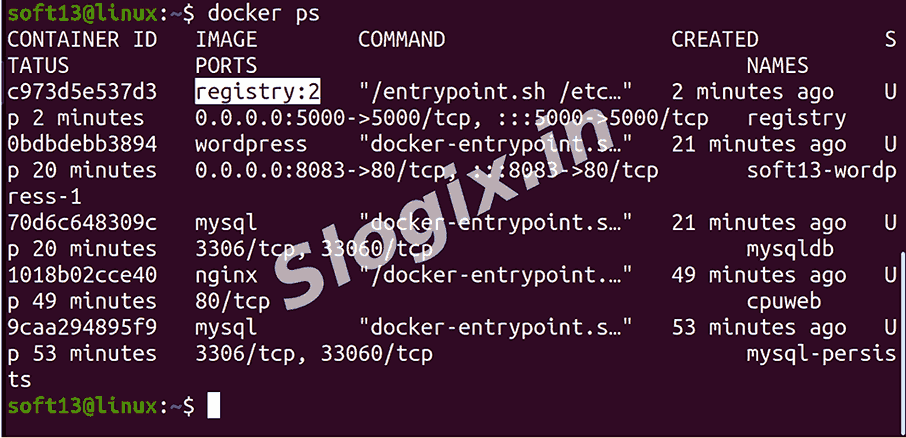
Step 1 — Check Registry Container is Running
Command:
docker ps
✔ You should see: registry:2 Up ...
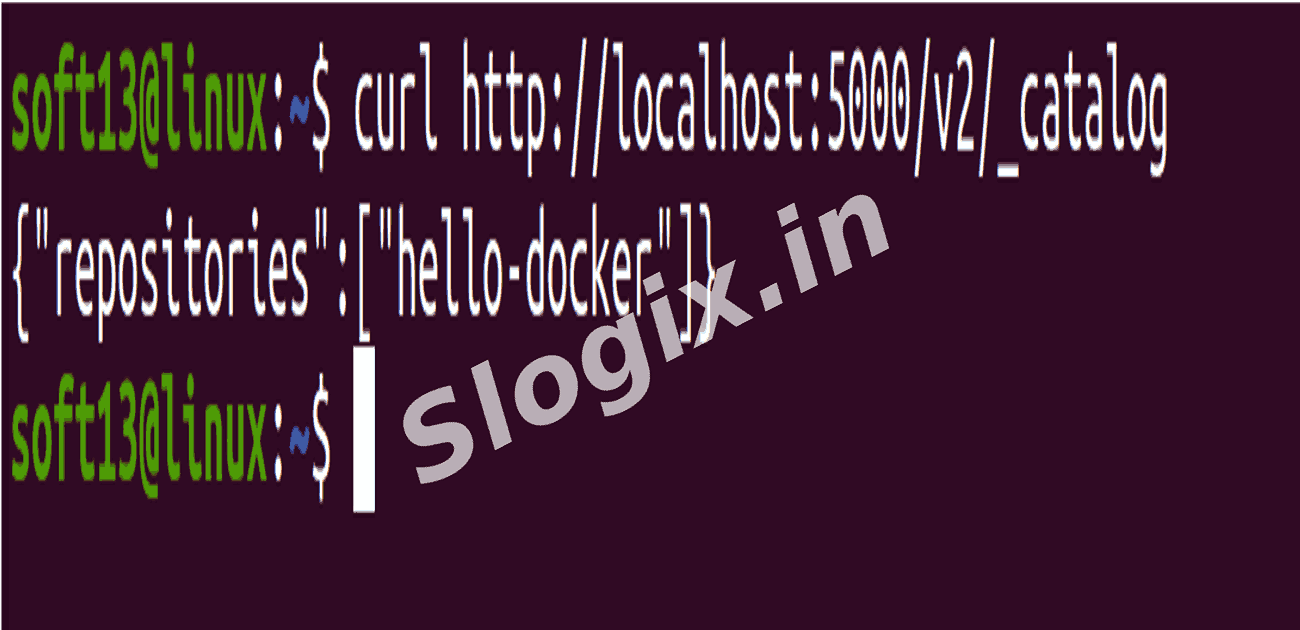
Step 2 — Check Stored Image in the Registry
Command:
curl http://localhost:5000/v2/_catalog
Expected output: {"repositories":["hello-docker"]}
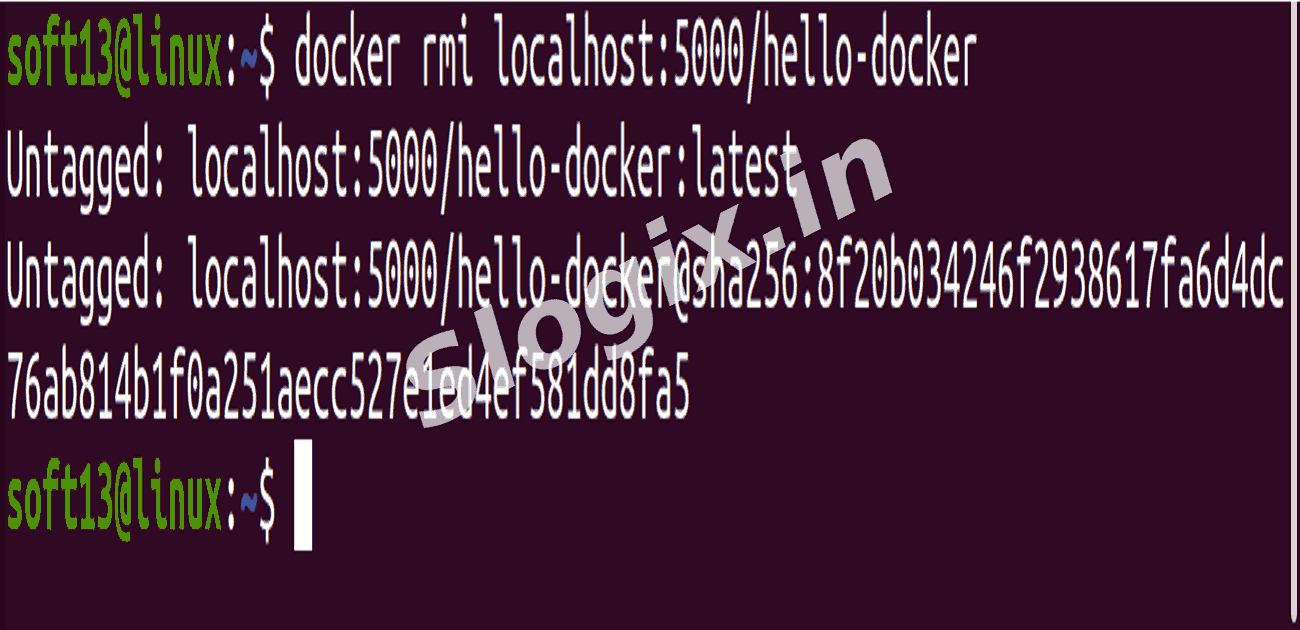
Step 3 — Remove Local Image and Pull Again to Verify
Commands:
docker rmi localhost:5000/hello-docker
docker pull localhost:5000/hello-docker
✔ If the pull succeeds, your registry works!
Step 4 — Try Running the Pulled Image
Command:
docker run localhost:5000/hello-docker
-
Outcome
✔ A functioning local Docker registry.
✔ Ability to push and pull images locally.
✔ Understand how organizations host private registries instead of relying on Docker Hub.