-
Step 1 — List Running Containers
Description: Before stopping or removing a container, identify its CONTAINER ID or name.
Command:
docker ps
Shows all currently running containers.
-
Step 2 — Stop a Container
Description: Stop a running container gracefully.
Command:
docker stop <container_id_or_name>
Example:
docker stop testcopyfile
The container will stop, but still exists on the system.
-
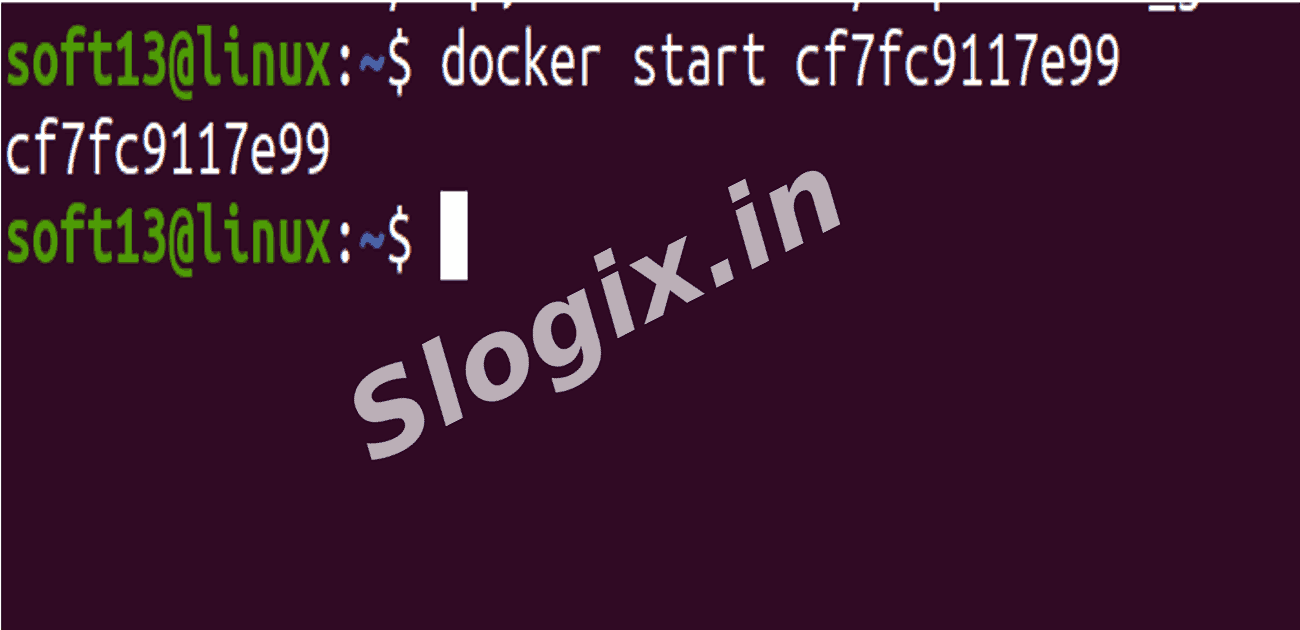
Step 3 — Start a Container
Description: Restart a stopped container.
Command:
docker start <container_id_or_name>
Example:
docker start testcopyfile
The container resumes running with the previous state.
-
Step 4 — Remove a Container
Description: Delete a container permanently. Make sure it is stopped before removing.
Command:
docker rm <container_id_or_name>
Example:
docker rm testcopyfile
The container is deleted, freeing disk space.
-
Step 5 — Verify Removal
Description: Check that the container no longer exists.
Command:
docker ps -a
The container should no longer appear in the list.
-
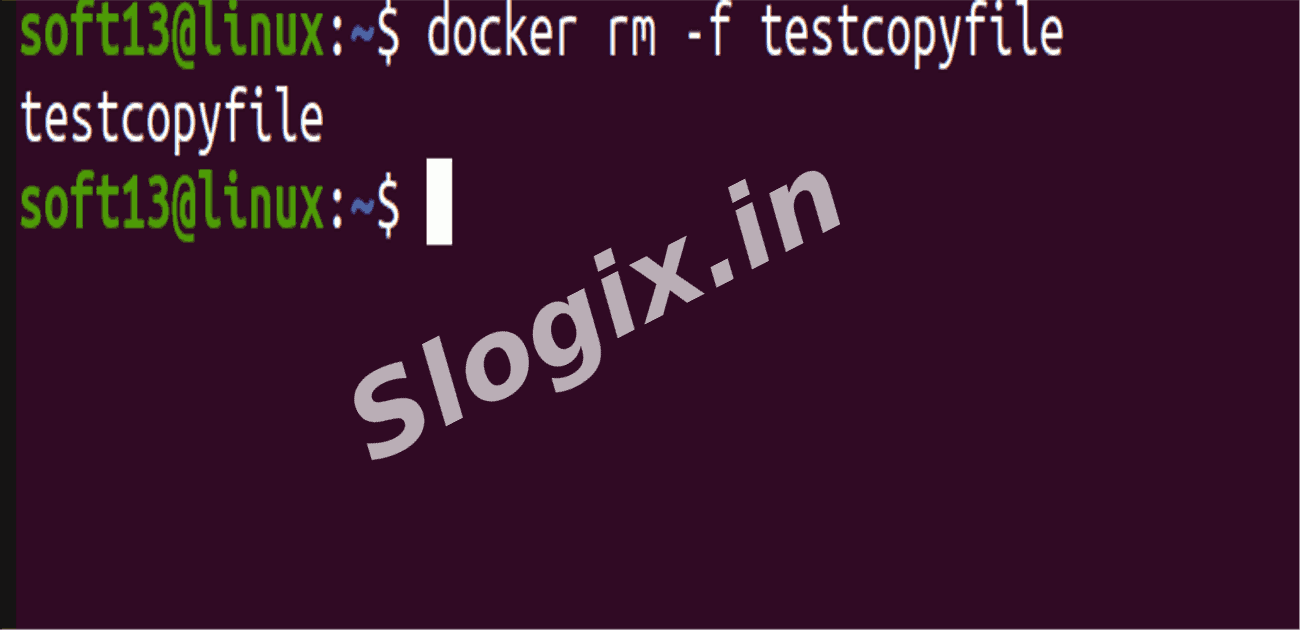
If you want to force remove a running container, you can use:
docker rm -f <container_id_or_name>
Always make sure you don’t need the container’s data before removal.