Research breakthrough possible @S-Logix
pro@slogix.in
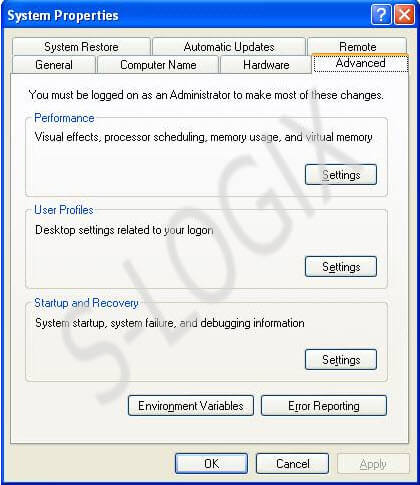
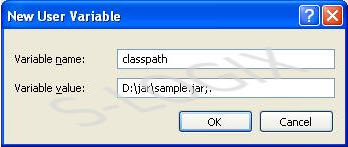
Steps for Setting Classpath path for jar file have been given below. During the compilation of java file, classes in the jar file will be referred even the jar file is located in any directory in the system if the classpath had been set in environment variable.